NEO BEHAVIORISM
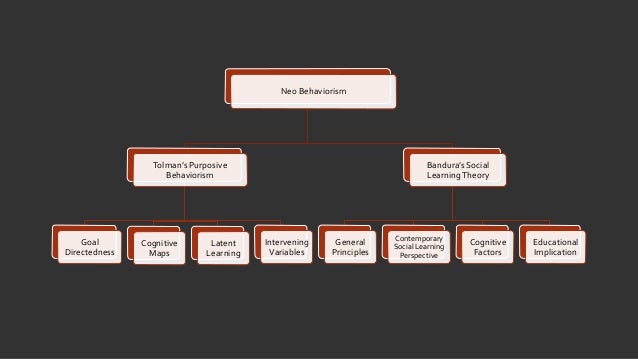
Neo Behaviorism- is a behavior cannot be full
understood simply in terms of observable stimuli and
reactions. Neo behaviorism introduce mediating
variables into the behaviorist stimulus-response
scheme.
Tolman's Purposive Behaviorism
Purposive Behaviorism
- it is also been referred to as Sign Learning
Theory and is often unite between behaviorism
and cognitive theory
Tolman believed that learning is a cognitive process.
Learning involves forming beliefs and obtaining
knowledge about the environment and then revealing
that knowledge through
purposeful and goal-directed behavior.
Tolman’s system was called purposive behaviorism because it studies behavior as it is organized around purposes.
TOLMAN'S KEY CONCEPT
- Learning is always purposive and goal- directed. Individuals act on beliefs, attitudes, changing conditions, and they strive towards goals. Tolman saw behavior as holistic, purposive, and cognitive. Cognitive map- learning the location of reward. Once an individual has learned where a given kind of reward is located, that location can often be reached by means other than those originally used.
- Latent Learning- whenever learning goes on without its being evident in performance at the time.
- The concept of intervening variable- these are not readily seen but serve as determinants of behavior.
- Reinforcement not essential for learning- Tolman concluded that reinforcement is not essential for learning, although it provides an incentive for performance.
General principles of social learning theory
1. Learn by observing.
2. Learning can occur through observation alone,
without a change in behavior.
3. Cognition plays a role in learning.
4. Transition between behaviorism and cognitive
learning theory
Contemporary Theory purposes that
reinforcement and punishment
- Contemporary Theory purposes that reinforcement and punishment have indirect effects on learning.
- Reinforcement and Punishment influence the result of individuals’ behavior that has been learned.
- The expectation of reinforcement influences cognitive processes.
Cognitive factors in social learning
- Learning without performance
- Cognitive processing during learning
- Expectations.
- Reciprocal causation
- Modeling
Educational implication of social learning theory
- Students often learn a great deal by simply observing other people.
- Describing the consequences of behavior can effectively increase the appropriate behaviors and decrease the inappropriate ones.
- Modeling provides an alternative to shaping for teaching new behaviors. Instead of using shaping, which is operant conditioning, modeling can provide a faster, more efficient means for teaching new behavior.
- Teachers and parents must model appropriate behaviors and take care that they do not model inappropriate behaviors.
- Teachers should expose students to a variety of other models. This technique is especially important to break down traditional stereotypes.
ALBERT BANDURA Social Learning Theory
Social Learning Theory Albert Bandura
Social Learning Theory- also called observational learning- theory that emphasizes learning through observation of others.We learn not only how to perform behavior but also what will happen to us in a specific situation if we do perform it
Types of Observational Learning Effects- INHIBITION - to learn not to do something that we already know how to do because a model being observed refrains from behaving in that way or does something-different from what is intended to be done.
- DIS INHIBITION - to learn to exhibit a behavior that is usually disapproved of by most people because a model does the same without being punished.
- FACILITATION – to be prompted to do something that is not ordinarily done because of insufficient motivation .
- OBSERVATIONAL LEARNING – to learn a new behavior pattern by watching and imitating the performance of someone else.
- Attention-mental focus or concentration Willingness of the child to observe and mimic the behavior of a model
- Retention-to encode the behavior in the memory ability to store information
- Production to actually perform the behavior observed.
- Motivation/Reinforcement -force that drives one to act
Three Forms of Reinforcement
- Direct Reinforcement-occurs when an individual watches a model perform, imitates that behavior and is reinforced or punished by some individual
- Vicarious Reinforcement-the observer anticipates receiving a reward for behaving in a given way because someone else has been so rewarded
- Self -Reinforcement-the individuals strives to meet personal standards and does not depend on or care about there action of others
My Reflection- i learned that learning is the result of associations forming between stimuli and responses,... we need to reinforce the pupils so that they can motivate and make what thing that they want in life and will make them better...
Thank youuuuuu po
TumugonBurahin